Buscar
-
Optimizing Mammogram Screenings: A Genetic Approach to a Personalized Screening Schedule
Breast cancer screening has long been a cornerstone of women's healthcare. With 1 in 8 women diagnosed with breast cancer in their lifetime1, the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has developed screening recommendations to help detect early-stage cancer. Notably in 2023, the USPSTF revised the recommended age for biennial mammogram screenings for women with average risk to start at age 40 instead of 502, estimated to result in 19% more lives being saved3 by starting screening earlier. While initiating screening at an earlier age offers advantages to a wide demographic, concerns about the potential of over-screening prompted research into the feasibility of identifying women with lower breast cancer risk who could safely delay mammograms. While guidelines address high-risk individuals, a notable gap exists in providing recommendations tailored to those at lower risk. To gain insight into a patient's risk level, physicians are able to utilize genetic testing to understand an individual's genetic makeup, providing precise insights into their predisposition to various health conditions, including breast cancer. Armed with this genetic information, healthcare providers could craft tailored screening strategies that align with an individual’s specific risk profile. This genetic risk-based approach underscores the value of genetics in individualizing the onset of screening to help avoid over-screening and its associated costs. Surprisingly, genetic information is not currently being widely utilized to identify women at risk of breast cancer or other diseases in clinical practice, despite its potential to make a significant positive impact for patients. A recent retrospective analysis of 25,591 women from the Healthy Nevada Project4 sheds light on the potential benefits of this genetic risk-based approach. The study classified 2,338 (9.1%) of these women as having a low genetic risk for breast cancer. What's remarkable is that these women exhibited a significantly lower and later onset of breast cancer compared to their average or high-risk counterparts. This finding suggests that it might be safe for low-risk women to delay mammogram screening by 5 to 10 years without compromising their health.
-
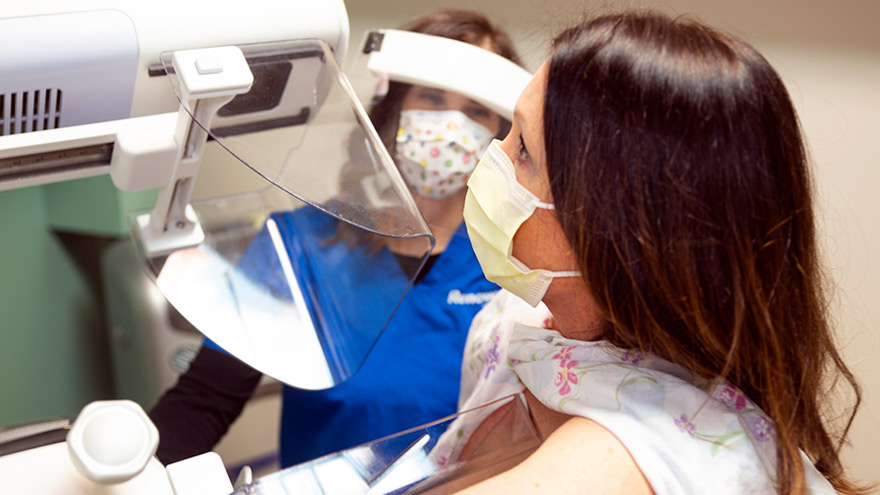
Ladies! Get Screened for Breast Cancer
Early detection is a significant piece of the breast cancer puzzle. Susan Cox, Renown Health Director of Cancer Operations, discusses what you need to watch for and how the latest technology can help detect potential cancer sooner. When should women start getting breast exams? It depends on risk factors: Average-risk women: Most medical organizations recommend the first mammogram between 40 and 44. Higher-risk women: Dependent on their high risk, which will dictate when they start screening, but generally around the age of 30 and not before 25 years old.
-
8 pruebas de evaluación de la salud importantes para hombres
Unfortunately, men are less likely to visit their doctor for exams, screenings, and consults than women. So with the help of Bonnie Ferrara, MD of Renown Health, we've put together a list of eight screenings to help men stay on top of their health game. 1. Blood Pressure Tests Ages 20+ Blood Pressure tests measure the pressure in your arteries as your heart pumps. Biennial (every two years) checks are recommended if you have normal blood pressure or more frequently if you have high blood pressure (hypertension) or low blood pressure (hypotension). The United States Preventative Services Taskforce cites normal blood pressure below 120 systolic (top number) and 80 diastolic (bottom number). 2. Cholesterol Screening Ages 20+ High levels of cholesterol increase your risk of stroke and heart disease. A simple blood test will help your healthcare provider determine your numbers and if you're at risk. If you have a family history of diabetes or heart disease, you may need yearly screenings. But, again, your doctor can provide the best course of action.
-
Prostate Cancer: Symptoms, Treatments and Screenings
Did you know: More than 2.9 million men in the United States who have been diagnosed with prostate cancer at some point are still alive today. Prostate cancer is common, but also treatable, especially when caught early. Dr. Michael Hardacre of the Renown Institute for Cancer explains. With the exception of skin cancer, prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed form of cancer in American men. In fact, the American Cancer Society offers these key statistics: About 1 man in 9 will be diagnosed with prostate cancer during his lifetime. Prostate cancer develops mainly in older men and in African-American men. About 6 cases in 10 are diagnosed in men aged 65 or older, and it is rare before age 40. The average age at the time of diagnosis is about 66. The good news: This form of cancer is very treatable when also detected early. Michael Hardacre, MD, radiation oncologist with Renown Institute for Cancer, is here to explain more about prostate cancer screenings and their role in early detection. What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland that only males have, and it makes part of the seminal fluid. Prostate cancer begins when the cells in the prostate gland start growing uncontrollably due to a change in the cell’s genes. Researchers are working to find what leads to the disease. Certain types of prostate cancer are hereditary, or passed on through genes. However, most types of prostate cancer are acquired and developed later in life. What are some of the signs of prostate cancer? Common signs of prostate cancer include: Frequent urination Weak urine flow Painful urination or inability to urinate Blood in urine or semen Painful ejaculation Erectile dysfunction If you notice any of these signs, talk with your primary care doctor. Although it may be intimidating to talk about any of these signs or symptoms, the earlier prostate cancer is detected, the better the options for treatment. How can you screen for or detect prostate cancer? The good news is that prostate cancer can often be found before symptoms appear, because screening is as simple as a blood test. Your doctor will look for levels of a prostate-specific antigen in the blood. If the results come back with anything concerning, then additional testing would be recommended. A transrectal ultrasound can also be used, which is usually painless and only takes about 10 minutes to complete. This exam gives the doctor an image of the prostate to measure its size, which can help determine the density of the prostate-specific antigen. If this test comes back with any suspicious results, then your doctor may recommend a biopsy. What are the treatment options? Depending on each case, treatment options for men with prostate cancer might include: Watchful waiting or active surveillance Surgery Radiation therapy Cryotherapy (cryosurgery) Hormone therapy Chemotherapy Vaccine treatment Bone-directed treatment It’s important to discuss all of the treatment option with your doctors, including goals and possible side effects, to help make the decision that best fits your needs. Some important things to consider when choosing a treatment option also include: The stage and grade of your cancer Your age and also your expected life span Any other serious health conditions you have Your feelings (and your doctor’s opinion) about the need to treat the cancer right away The likelihood that treatment will cure your cancer (or help in some other way) Your feelings about the possible side effects from each treatment Renown Institute for Cancer | 775-982-4000 At the Renown Health Institute for Cancer, our experienced team provides the support and care to maintain the highest quality of life and then achieve the best possible outcome, all in one location that’s close to home. Our dedicated team, clinical expertise and also advanced treatment options allow us to tailor care to each patient. Learn about: Our Team Cancers We Treat Screening and Prevention Treatment Options
Read More About Prostate Cancer: Symptoms, Treatments and Screenings
-
3D vs Whole Breast Ultrasound Which is Right for You
Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in women in the U.S. That’s why early detection is so important. Dr. George Krakora, a radiologist with Renown Institute for Cancer, explains what to watch for and how new technology can lead to early detection. Most women know the importance of breast health and staying current with annual breast exams, but may not know that both screening guidelines and technology is evolving. So we asked George Krakora, MD, a radiologist for the Renown Institute for Cancer, what every woman should know about breast cancer detection and which screening method is right for them. First off, when should women start getting breast exams? Generally, women should start getting breast exams using mammography or ultrasound after they turn 40 years old. But we also want women ages 18 to 39 to talk to their primary care provider and ask for what’s called a formal risk assessment to see if screening is needed sooner. And you want to make sure your care provider is giving you a breast exam starting at age 25. It’s also a good idea to be familiar with how your breasts look and feel so you can report any changes to your care provider. What are the risk factors for breast cancer? Are there any preventive steps women can take? There a few risk factors you can’t control, like your age, family history of breast or other cancers, and if you have dense breast tissue. Your risk for breast cancer increases as you get older, and most breast cancers are diagnosed after age 50. Knowing your family history is important because a history of cancer and shared lifestyle can raise your risk. Your breast density can also increase your risk: Women with high breast density are four-to-five times more likely to get breast cancer than women with low breast density. But the good news is there are quite a few things you can do to prevent breast cancer, like not smoking, watching your alcohol intake, and maintaining a healthy weight with good diet and exercise. There are a lot of newer screenings out today. What is the difference between 2-D and 3-D mammography? In a 2-D mammogram, the tech takes X-rays of the breast. These pictures can show the radiologist if there are any lumps or tumors you might not be able to feel. In 3-D mammography, the process is largely the same but more X-rays are taken and it takes a few seconds longer for each image. This kind of exam detects 41 percent more cancers and reduces the number of false-positive results given to patients. This improvement in technology is great for both patients and their care providers. 3-D mammography provides better images of the breast, which allow doctors to more clearly diagnose and avoid false positives, especially in women with dense breast tissue. And what about a whole breast ultrasound. What is that? A whole breast ultrasound uses sound waves to detect cancerous tumors in the breast without using any radiation — it’s an ultrasound just like pregnant women get to check up on their baby. And the exam only takes about 20 minutes. We recommend these exams for patients whose mammograms have shown that they have dense breast tissue. Dense breast tissue can make it harder for doctors to see any abnormalities, lumps or tumors in a mammogram, so this technology ensures better early detection.
Read More About 3D vs Whole Breast Ultrasound Which is Right for You