Buscar
-
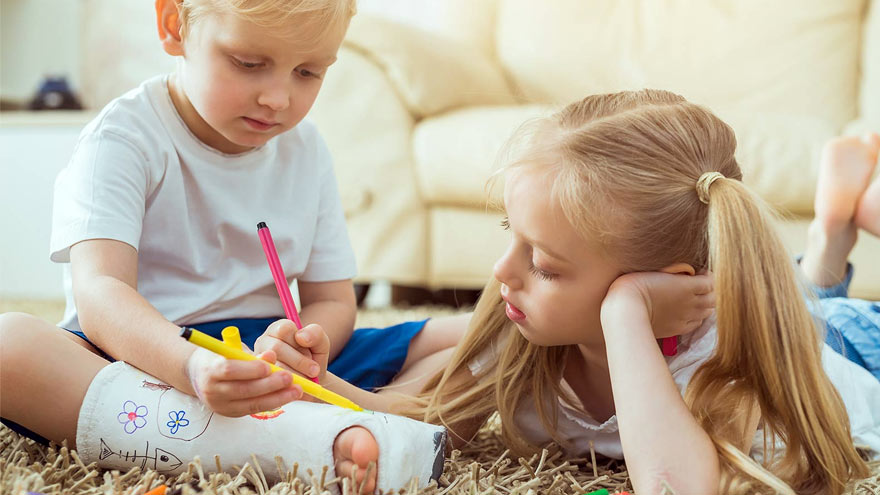
Bone Fractures in Children Honest Expert Advice
Michael Elliott, MD, head of the Department of Pediatric Orthopedics and Scoliosis, answers some common questions about bone fractures. Is there a difference between broken bones and fractures? No, these are two different names for the same injury. Of course the common term is a broken bone. Using either name will describe your concerns. Medical personnel typically describe a broken bone as a fracture to a specific bone. For example, a broken wrist is also a fractured distal radius. To clarify, this describes the injured bone and the precise location. How do I know if my child has broken their bone? Many times children will fall and complain of their arm or leg hurting. In most cases the pain goes away and the child will return to their activities. When there is a deformity to the limb (curve in arm) and the child is complaining of pain, it is probably a fracture. If the arm or leg looks straight, look to see if there is any swelling or bruising. Both are signs of a possible fracture. Finally, if the limb looks normal but the child continues to complain, gently push on the bone. Likewise if it causes the same pain, then they likely have a fracture and should have an x-ray. My child fractured their growth plate, what does this mean? Growth comes from this area of the bone. In detail, these are located all over the body but typically at the end of the bones. With this in mind, fractures to these areas can result in the bone growing abnormally. Because of potential shortening of the arm or leg, or bones growing crooked, it is important to follow fractures closely (up to 1-2 years or longer). It is better to identify a problem early. Small problems can be treated with small surgeries. What if the bones of the x-ray do not line up? Because children are growing, unlike adults, their bones will remodel and straighten with growth. The amount of remodeling occurring depends on a child’s age, the bone fractured and the location. In many cases an angled bone will grow straight over the course of a year. For this reason, someone with experience in caring for children needs to follow bone growth. How long does it take fractures to heal? Factors deciding when a cast can come off include: Child’s age. Bone fractured. Fracture location. Young children heal faster than teens, teens heal faster than young adults, who heal faster than older adults. In young children most fractures heal in 4-6 weeks. However, teens generally take 6 weeks to heal, and adults can take much longer. Although your child is out of their cast, it may not be healed completely to return to all activities. Placing a splint is during this time is common. This typically gives them added protection for several weeks after their cast is removed - in case they forget their limitations. What if my child is still limping? Whether a child is in a walking or non-weight bearing cast, removing it often leaves them stiff and sore. Therefore many children will walk as though they still have a cast in place. In most cases this resolves in about three weeks. Regardless, if your child is still limping or walking abnormally after three weeks, contact the treating doctor. They may benefit from physical therapy or a repeat evaluation. (This article was original published in the July 2019 issue of South Reno Kids & Sports.)
Read More About Bone Fractures in Children Honest Expert Advice
-
Head, Neck and Oral Cancers: How You Can Spot and Treat Them
Head, neck and oral cancers account for just 3 percent of all cancer in the U.S. and can be hard to diagnose. Dr. Abhinand Peddada, radiation oncologist with the Renown Institute for Cancer, explains. While you likely don’t frequently hear about head, neck and oral cancers — they are significantly less common than many kinds of cancer — they can be extremely dangerous. One of the primary reasons: some symptoms mimic the common cold, making them difficult to detect without a medical professional. We asked Abhinand Peddada, M.D., radiation oncologist with the Renown Institute for Cancer, to break down the symptoms and lifestyle risks of these rare cancers. First off, what are some of the signs and symptoms of head, neck and oral cancers? Symptoms can vary based on where the cancer is. For example, throat cancer may show up as a persistent sore throat, while sinus cancer may present as soreness or pressure in the sinuses that doesn’t get better. Some other symptoms to watch may include: Swelling in the throat Painless swelling in the neck Red or white patches in the throat Hoarseness Bloody noses or blood in the mucus or saliva A new and unexplained lump or bump anywhere on the face, neck, mouth or throat Difficulty breathing Difficulty swallowing, chewing or moving the muscles in your face, neck, mouth or throat Bad breath, even with good oral hygiene Loose teeth Dentures or retainers that no longer fit Double vision Who is most at risk for head, neck and oral cancers? Both men and women can develop head, neck and oral cancers, but men are at almost twice the risk of women. People over the age of 40 are also at a higher risk, and these cancers tend to be more common in African Americans. Tobacco use — including cigarettes, cigars, pipes and chewing tobacco — is another risk factor. Tobacco is linked to 85 percent of head and neck cancers. Exposure to fumes and chemicals can increase your risk as well. We’re also seeing more HPV-related head and neck cancers in the U.S., so patients with HPV may want to watch more closely for symptoms. What about screening and prevention? Your dentist already looks for signs and symptoms at your regular dental checkups. Additionally, if you have one of these risk factors and are experiencing signs and symptoms, it’s a good idea to check with your doctor about possible screenings. To help prevent these types of cancers, try to minimize your controllable risk factors. This means quitting tobacco, watching your alcohol consumption and taking care of your oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly. We also recommend the HPV vaccination for both boys and girls starting at age 11. By vaccinating at an earlier age, one is less likely to develop oral HPV. What do diagnosis and treatment look like for these cancers? At Renown Institute for Cancer we offer the most advanced diagnostic testing available including fiberoptic photos, CT and PET scans, as well as MRIs. Together, you and your care team will decide which treatment best fits your needs. For these types of cancers, treatment options include radiation, chemotherapy and surgery. Renown Institute for Cancer | 775-982-4000 At the Renown Health Institute for Cancer, our experienced team provides the support and care to maintain the highest quality of life and then achieve the best possible outcome, all in one location that’s close to home. Our dedicated team, clinical expertise and advanced treatment options allow us to tailor care to each patient. Learn about: Our Team Cancers We Treat Screening and Prevention Treatment Options Find a Cancer Doctor
Read More About Head, Neck and Oral Cancers: How You Can Spot and Treat Them